All About UTP Cable Wiring
What is UTP Cable?
UTP stands for Unshielded Twisted Pair cable. UTP cable is a 100 ohm copper cable that consists of 2 to 1800 unshielded twisted pairs surrounded by an outer jacket. They have no metallic shield. This makes the cable small in diameter but unprotected against electrical interference. The twist helps to improve its immunity to electrical noise and EMI.


UTP CABLE APPLICATIONS
UTP cables are mostly used for LAN networks. They can be used for voice, low-speed data, high-speed data, audio and paging systems, and building automation and control systems. UTP cable can be used in both the horizontal and backbone cabling subsystems.
UTP CABLE CATEGORIES AND PERFORMANCE SPECIFICATIONS
UTP cables were invented for voice applications. Voice UTP cables only needed to carry analog signals which are very robust and not easily corrupted by electrical noise or EMI. However, as UTP cables were used for different systems, higher quality UTP cables were required to support data systems that used digital signaling.
As the applications evolved, different categories or grades of UTP cables were created along these years. Higher category UTP cables are referred to as data grade UTP cables, and low category UTP cables are referred to as voice grade UTP cables.
The following table shows different Category UTP cables, their business applications and corresponding performance specification.
| Category | Grade | Business Application | Frequency Range |
| Category 1 | voice grade | voice-grade telephone networks only; not for data transmissions | 750 kHz |
| Category 2 | voice grade | voice-grade telephone networks, as well as IBM dumb-terminal connections to mainframe computers | 1 MHz |
| Category 3 | data grade | voice-grade telephone networks, 10Mbps Ethernet, 4Mbps Token Ring, 100BaseT4 Fast Ethernet, and 100VG Any LAN | 16 MHz |
| Category 4 | data grade | 16Mbps Token Ring networks | 20 MHz |
| Category 5 | data grade | 100BastTX Fast Ethernet, SONET, and OC-3 ATM networks | 100 MHz |
| Category 5e | data grade | Gigabit (1000Mbps) Ethernet | 100 MHz |
| Category 6 | data grade | Gigabit (1000Mbps) Ethernet | 250 MHz |
| Category 6A | data grade | Gigabit (1000Mbps) and 10 Gigabit Ethernet | 500 MHz |
Ethernet Cable Pin Outs:
There are two basic ethernet cable pin outs. A straight through ethernet cable, which is used to connect to a hub or switch, and a crossover ethernet cable used to operate in a peer-to-peer fashion without a hub/switch. Generally all fixed wiring should be run as straight through. Some ethernet interfaces can cross and un-cross a cable automatically as needed, a handy feature.
.aspx)
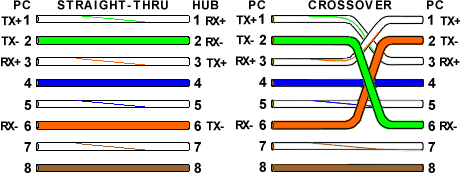
Standard, Straight-Through Wiring
| RJ45 Pin # | Wire Color (T568A) | Wire Diagram (T568A) | 10Base-T Signal 100Base-TX Signal | 1000Base-T Signal |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | White/Green | Transmit+ | BI_DA+ | |
| 2 | Green | Transmit- | BI_DA- | |
| 3 | White/Orange | Receive+ | BI_DB+ | |
| 4 | Blue | Unused | BI_DC+ | |
| 5 | White/Blue | Unused | BI_DC- | |
| 6 | Orange | Receive- | BI_DB- | |
| 7 | White/Brown | Unused | BI_DD+ | |
| 8 | Brown | Unused | BI_DD- |
Crossover Cable Wiring Diagram
| RJ45 Pin # (END 1) | Wire Color | Diagram End #1 | RJ45 Pin # (END 2) | Wire Color | Diagram End #2 |
| 1 | White/Orange |  | 1 | White/Green |  |
| 2 | Orange |  | 2 | Green |  |
| 3 | White/Green |  | 3 | White/Orange |  |
| 4 | Blue |  | 4 | White/Brown |  |
| 5 | White/Blue |  | 5 | Brown |  |
| 6 | Green |  | 6 | Orange |  |
| 7 | White/Brown |  | 7 | Blue |  |
| 8 | Brown |  | 8 | White/Blue |  |
Note: The crossover ethernet cable layout is suitable for 1000Base-T operation, all 4 pairs are crossed.