Redundant Array of Independent Disks (RAID)
What is RAID
Redundant Array of Independent Disks (RAID) is a virtual disk technology that combines multiple physical drives into one unit. It allows storing data across multiple hard drives. RAID can create redundancy, improve performance, or do both.
RAID should not be considered a replacement for backing up your data. If critical data is going onto a RAID array, it should be backed up to another physical drive or logical set of drives.
A RAID system consists of two or more drives working in parallel. These can be hard discs, but there is a trend to also use the technology for SSD (Solid State Drives).
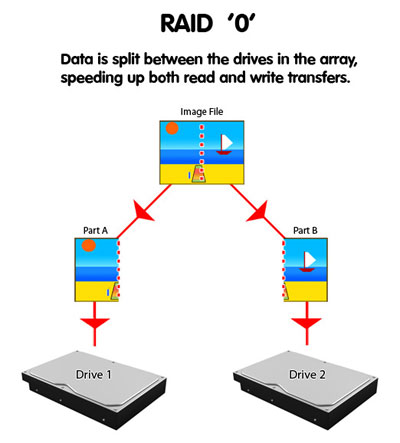

The following are terms that are normally used in connection with RAID:
- Striping: data is split between multiple disks.
- Mirroring: data is mirrored between multiple disks.
- Parity: also referred to as a checksum. Parity is a calculated value used to mathematically rebuild data.